I learned about Apache Sedona while working at my previous company. That company had a product that relied heavily on spatial data, so the data team worked on processing spatial datasets to help improve the product.
At that time, the team often used GeoPandas for spatial analysis. GeoPandas is quite popular, has proper documentation, and there are many forums discussing how to use it.
However, since the spatial data we processed was quite large, I realized there would be bottlenecks if we kept using GeoPandas, it’s just too slow when handling big datasets. So I started looking for a framework that supports distributed computing for spatial data processing.
That’s when I found Apache Sedona. It’s similar to GeoPandas in how you work with it, but much faster because it’s built on top of Apache Spark.
Previously, my company used Databricks, so I helped set up Apache Sedona on Databricks.
For installation on local or on-premise environments, here’s what you need to do:
Make sure Apache Spark and Java are installed.
Install the Apache Sedona library:
pip install apache-sedona[spark]- Prepare the Sedona JAR file, you need to download it and place it in the Spark directory
You can read the full documentation here:
https://sedona.apache.org/latest/setup/install-python/
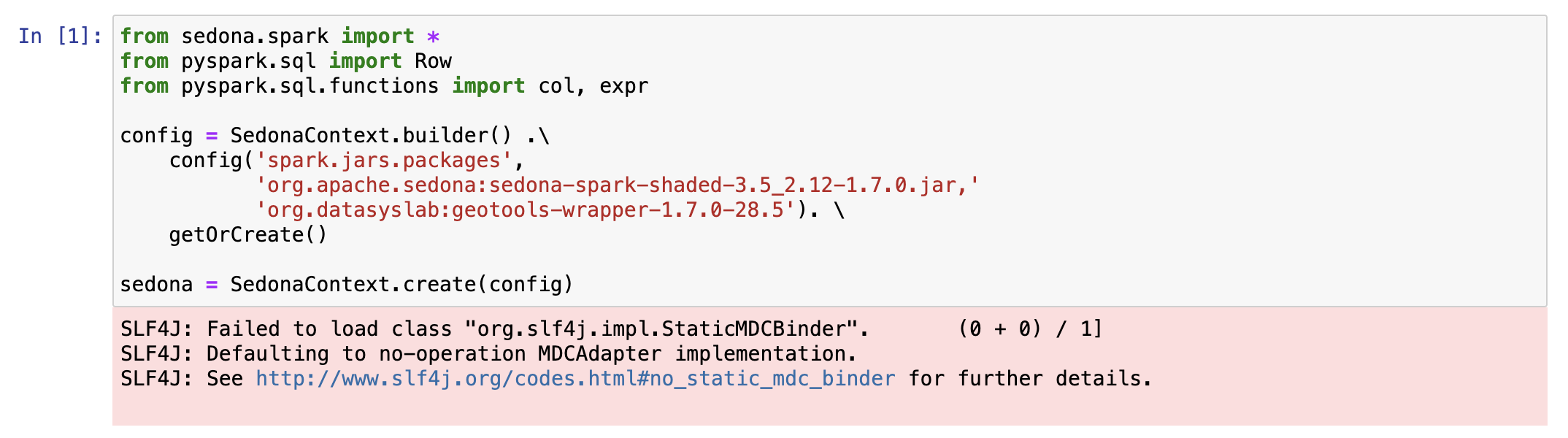
This is the example using sedona, I'm trying to create sedona context first:

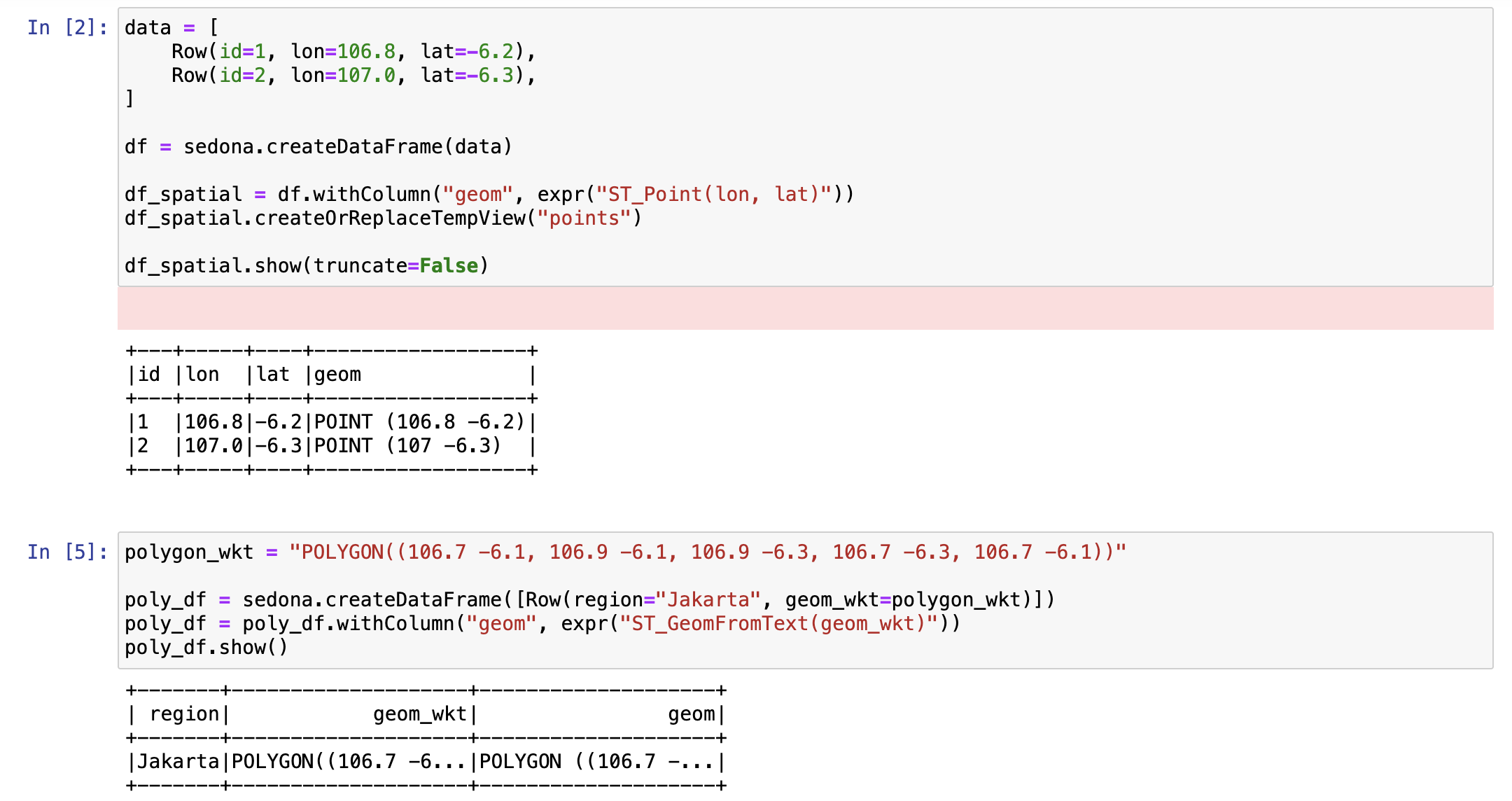
And then, Let's try to create simple dataframe using spatial function:
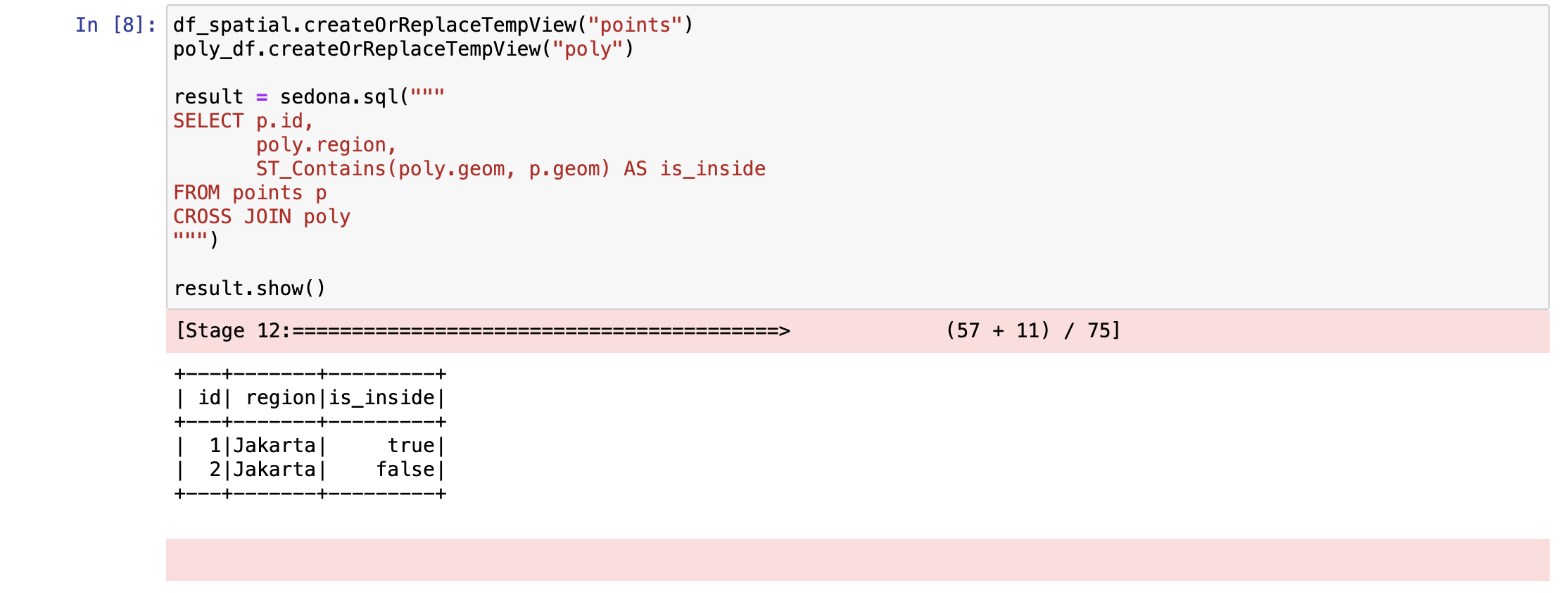
We can use more spatial function on sedona like ST_Contains, this is the example:
Apache Sedona is an interesting spatial framework and much faster than GeoPandas, but I think the focus is a bit different.
GeoPandas is great for exploration and plotting, and it can easily create visualizations.
Sedona, on the other hand, is focused on faster processing of spatial data.
Both Sedona and GeoPandas have their own strengths when working with spatial data.