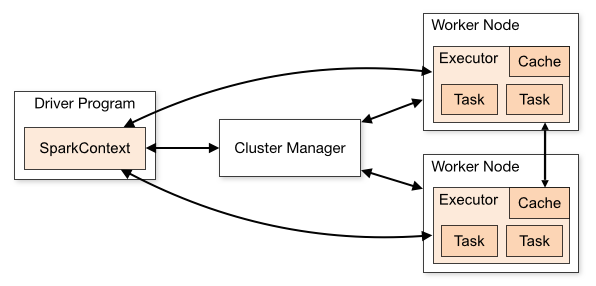
Spark is an engine for processing large scale data. It usually has two main components: the master node and the worker nodes.
The master node is responsible for dividing jobs and communicating with the cluster manager to allocate resources. Meanwhile, the worker nodes are responsible for running the tasks assigned by the master.
The connection between the master and the workers is handled by the cluster manager. It is responsible for managing resources, deciding where to execute jobs, and selecting which nodes will run the executors.
Here is an example of Spark architecture, I found this image on google.
There are several types of cluster managers:
- Standalone
- Hadoop YARN
- Kubernetes
- Apache Mesos
Another key concept in Spark is lazy evaluation. Spark only executes computations when an action command is triggered, such as `show`, `count`, or `collect`.
This is different from Pandas. For example:
df = pd.read_csv("YOUR_FILE_PATH")That command immediately loads the data and consumes memory.
In spark,
df = spark.read.csv("YOUR_FILE_PATH")This command does not load anything yet. The actual processing only happens when you run:
df.show()